Lab Guide: Exploring Agentic AI using LlamaStack Playground
1. Setup
In the previous section we explored llama stack agents via Jupyter notebooks. In the next part we want to use the agents via a UI.
Llama stack can be integrated in any Web Interface as it is at its core an API. For the next steps we are going to use the Llama Stack playground, a Python Streamlit based UI that is part of the Llama Stack Github repository.
Save the following block which contains all necessary CRs to a llama-stack-playground.yaml file and run oc apply -f llama-stack-playground.yaml, after which you will be able to access the playground via created route.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: llama-stack-playground
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: llama-stack-playground
namespace: llama-stack-playground
annotations:
serviceaccounts.openshift.io/oauth-redirectreference.primary: '{"kind":"OAuthRedirectReference","apiVersion":"v1","reference":{"kind":"Route","name":"llama-stack-playground"}}'
---
apiVersion: authorization.openshift.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: system:openshift:scc:anyuid
roleRef:
name: system:openshift:scc:anyuid
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: llama-stack-playground
namespace: llama-stack-playground
userNames:
- system:serviceaccount:llama-stack-playground:llama-stack-playground
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: llama-stack-playground
namespace: llama-stack-playground
annotations:
service.alpha.openshift.io/serving-cert-secret-name: proxy-tls
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- name: proxy
port: 443
targetPort: 8443
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: llama-stack-playground
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: llama-stack-playground
namespace: llama-stack-playground
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: llama-stack-playground
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: llama-stack-playground
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: llama-stack-playground
spec:
serviceAccountName: llama-stack-playground
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1001
containers:
- name: oauth-proxy
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
readOnlyRootFilesystem: false
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1001
image: registry.redhat.io/openshift4/ose-oauth-proxy-rhel9@sha256:f55b6d17e2351b32406f72d0e877748b34456b18fcd8419f19ae1687d0dce294
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 8443
name: public
args:
- --https-address=:8443
- --provider=openshift
- --openshift-service-account=llama-stack-playground
- --upstream=http://localhost:8501
- --tls-cert=/etc/tls/private/tls.crt
- --tls-key=/etc/tls/private/tls.key
- --cookie-secret=SECRET
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/tls/private
name: proxy-tls
- name: llama-stack-playground
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
readOnlyRootFilesystem: false
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 1001
image: "quay.io/rh_ee_anixel/llama-stack-playground:0.0.4"
command:
- streamlit
- run
- /llama_stack/core/ui/app.py
imagePullPolicy: Always
ports:
- containerPort: 8501
name: http
protocol: TCP
env:
- name: STREAMLIT_BROWSER_GATHER_USAGE_STATS
value: "false"
- name: STREAMLIT_SERVER_ADDRESS
value: "0.0.0.0"
- name: STREAMLIT_SERVER_PORT
value: "8501"
- name: LLAMA_STACK_ENDPOINT
value: "http://llamastack-with-config-service.llama-stack:8321"
- name: DEFAULT_MODEL
value: "granite-31-2b-instruct"
livenessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /
port: http
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 5
readinessProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
httpGet:
path: /
port: http
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5
timeoutSeconds: 3
resources:
limits:
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 500m
memory: 512Mi
volumes:
- name: proxy-tls
secret:
secretName: proxy-tls
---
apiVersion: route.openshift.io/v1
kind: Route
metadata:
name: llama-stack-playground
namespace: llama-stack-playground
spec:
to:
kind: Service
name: llama-stack-playground
weight: 100
port:
targetPort: proxy
tls:
termination: reencrypt
insecureEdgeTerminationPolicy: RedirectOpen up the following url within a browser of your choice (accept the authentication via OpenShift oauth server) to interact with the Llama Stack Playground:
echo $(oc get route llama-stack-playground -n llama-stack-playground -o jsonpath='{.spec.host}')2. Disclaimer
|
Because we’re using models provided through MaaS (Models-as-a-Service), some tasks may not work perfectly on the first attempt. If that happens, simply retry a few times to achieve the expected result. Remember, the goal of this lab isn’t to produce a flawless solution, but to help you become familiar with the core concepts of agentic AI. |
3. Chat via Llama Stack Playground
Use the Chat section of the Llama Stack Playground to chat with the two available models. The chat functionality doesn’t use the memory capability of Llama Stack, so
each message is handled indivudaly. You can adapt the system configuration and see the impact on the models:
4. Agentic AI via Llama Stack Playground
Use the Tools section of the Llama Stack Playground to use the agent capabilities of Llama Stack together with the configured tools. You can do the same examples as with
the agents defined within the Jupyter notebooks in the second part of this lab. As we are using the agent capabilities
the history of the prompts is now available within every prompt.
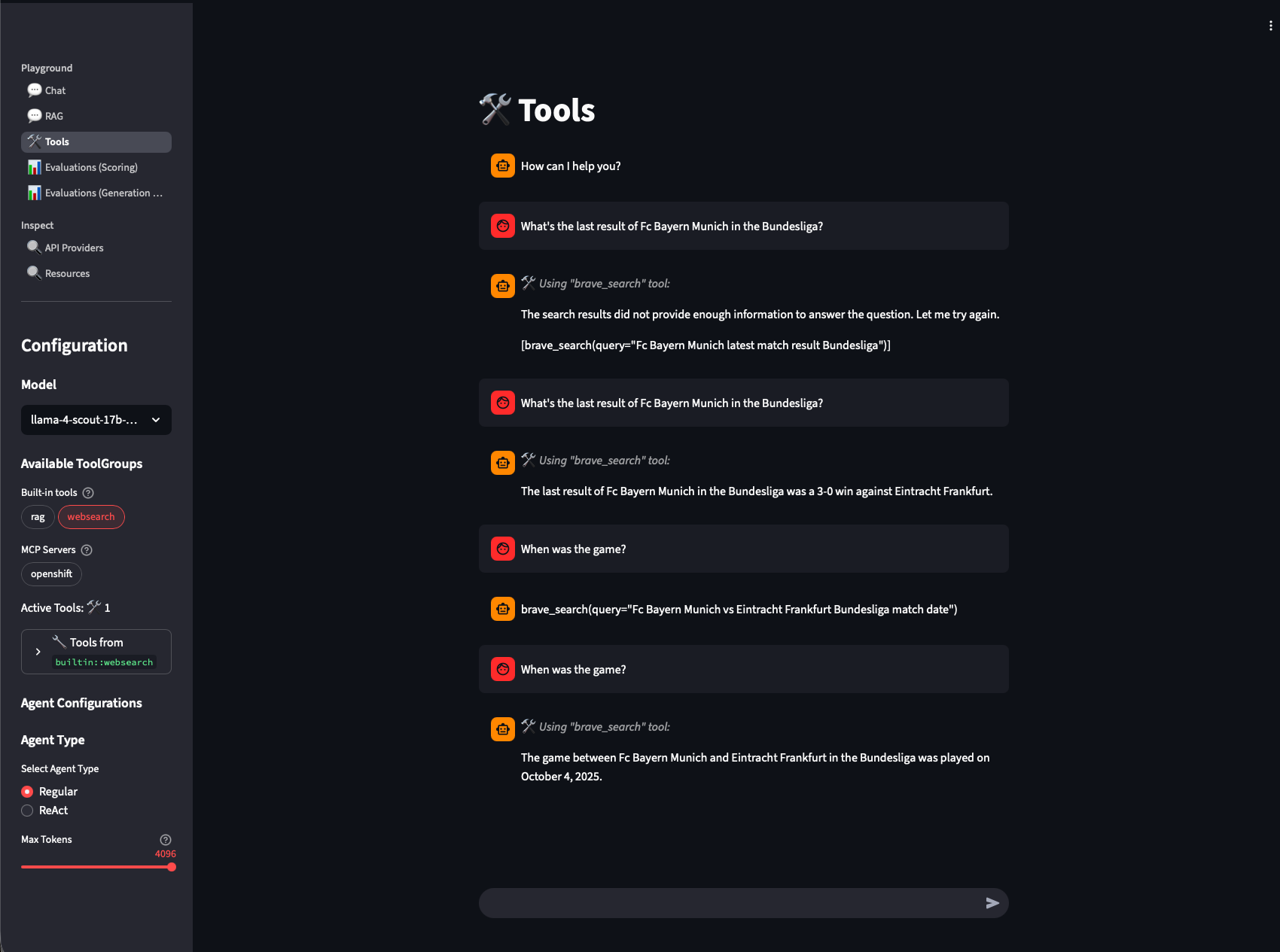
In the following example you can see the usage of the websearch tool:
|
In the screenshot, you can also see a common issue with Agentic AI. Twice, the model attempts to use the brave_search tool (the web search tool), but the response format is incorrect, so the agent doesn’t actually trigger the web search. In the UI, you can tell whether a tool call was executed by checking if the ⚒️ icon is displayed. After the question is asked again, the model’s response is formatted correctly, the brave_search tool is successfully invoked, and the agent provides the correct answer to the user. |
5. Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) via Llama Stack Playground
In the next step we are going to explore Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) via the Llama Stack Playground. With RAG its possible to add context from vectorized input to the user prompts.
First we need to fill the vector database that we deployed with the llama stack server with content.
Download the Red Hat OpenShift AI Self-Managed 2.24 documentation as pdf.
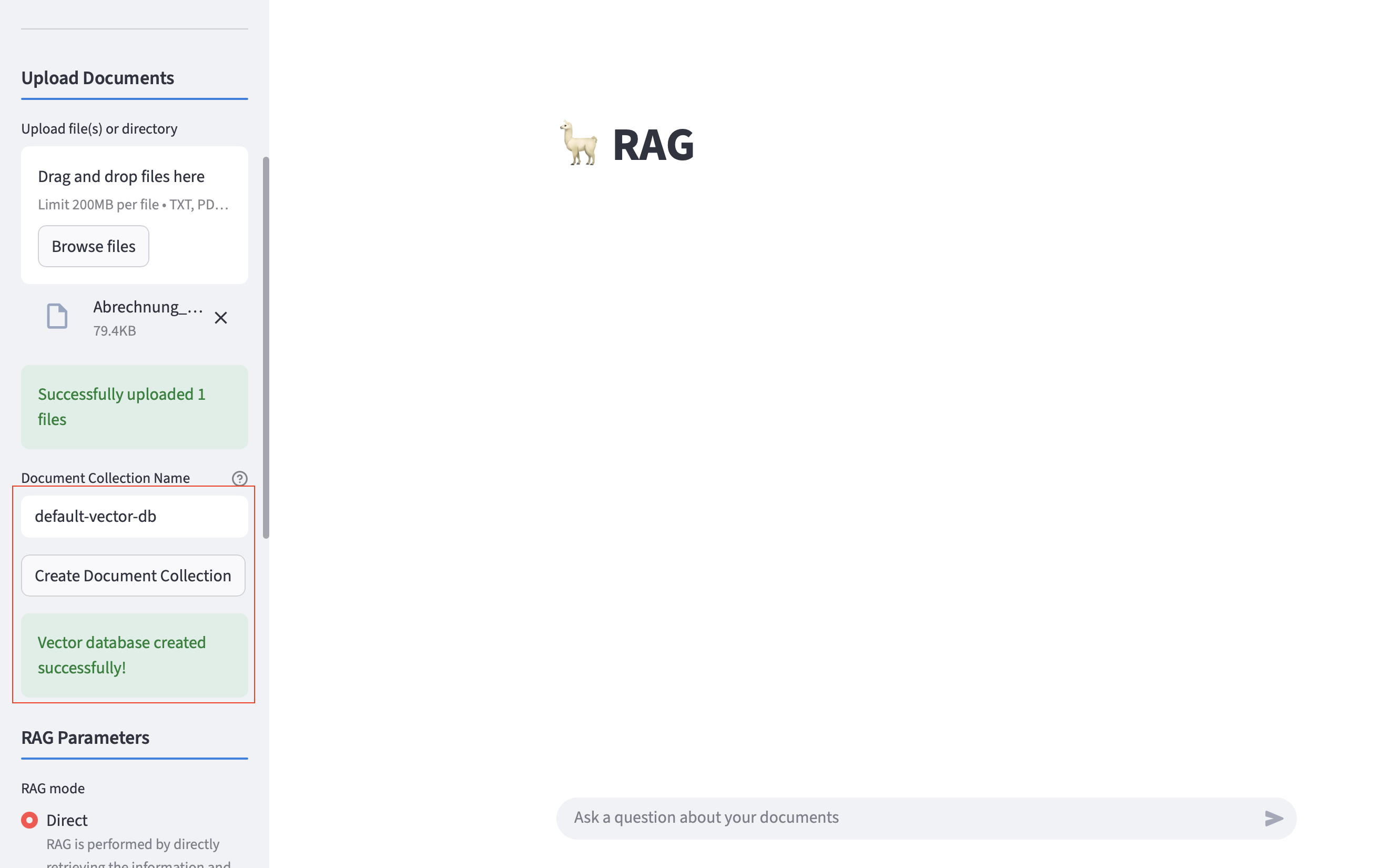
Use the RAG section to upload the PDF. You need to follow this steps:
-
Click on
Browse Fileand select the RHAOI documentation. -
Enter
default-vector-dbinside the document collection name. -
Click on
Create Document Collectionto store the document inside the vector database. -
Wait until you see the
Vector database created successfully!message. This can take up to 3 minutes. You can also check the logs of the llama stack pod inside thellama-stacknamespace to see the progress.
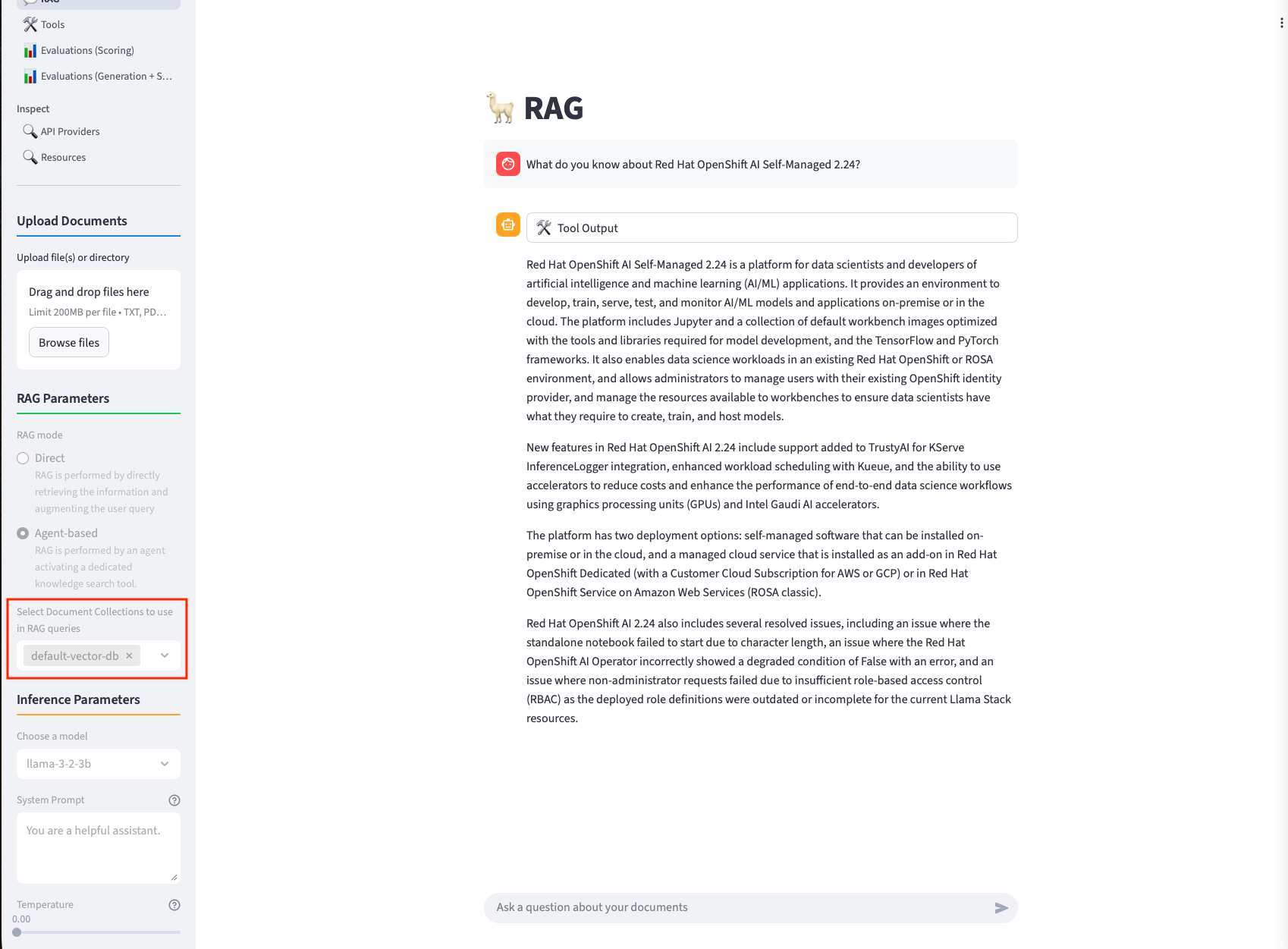
Now you can scroll down and ask questions about the content of the document. The model will get context from the vector db and answer the question based on it:
-
Make sure to select the
default-vector-dbcollection to be used within the RAG Parameter section. -
You can either use
DirectorAgent-basedRAG.
|
Within a customer scenario the default upload is done via pipelines, while it is still able to upload additional content by the user. |
6. Bonus - Llama Stack ReAct Agent & System Prompts
With the agents we’ve used so far, we haven’t customized the system prompts much or added specific behavioral instructions. However, doing so can make a tremendous difference in the efficiency and reliability of an agentic system.
For example, in the Jupyter notebook section of the lab, we defined the following agent:
agent_mcp_ocp = Agent(
client_mcp_ocp,
model="llama-3-2-3b",
instructions="You are a helpful assistant",
tools=[
"mcp::openshift"
],
max_infer_iters=5,
sampling_params={
"strategy": {"type": "top_p", "temperature": 0.1, "top_p": 0.95},
"max_tokens": 8000,
},
)
session_mcp_ocp = agent_mcp_ocp.create_session("monitored_session")Here, we only provided a minimal system prompt — "You are a helpful assistant." Each time the model processes a request, Llama Stack combines this system prompt with the tool definitions and the current chat history before sending it to the model. This default behavior works, but it doesn’t give the agent much structure or context for complex multi-step reasoning.
In contrast, more sophisticated setups — such as the ReAct agent included in the Llama Stack Python client — use a much larger and more structured system prompt. Read through the default system prompt for it here. The ReAct prompt enforces a single, machine-readable JSON output per turn with three required fields: thought, action, and answer. It also includes detailed rules and examples, ensuring the model’s tool usage and reasoning steps are consistent and easy for the orchestrator to interpret.
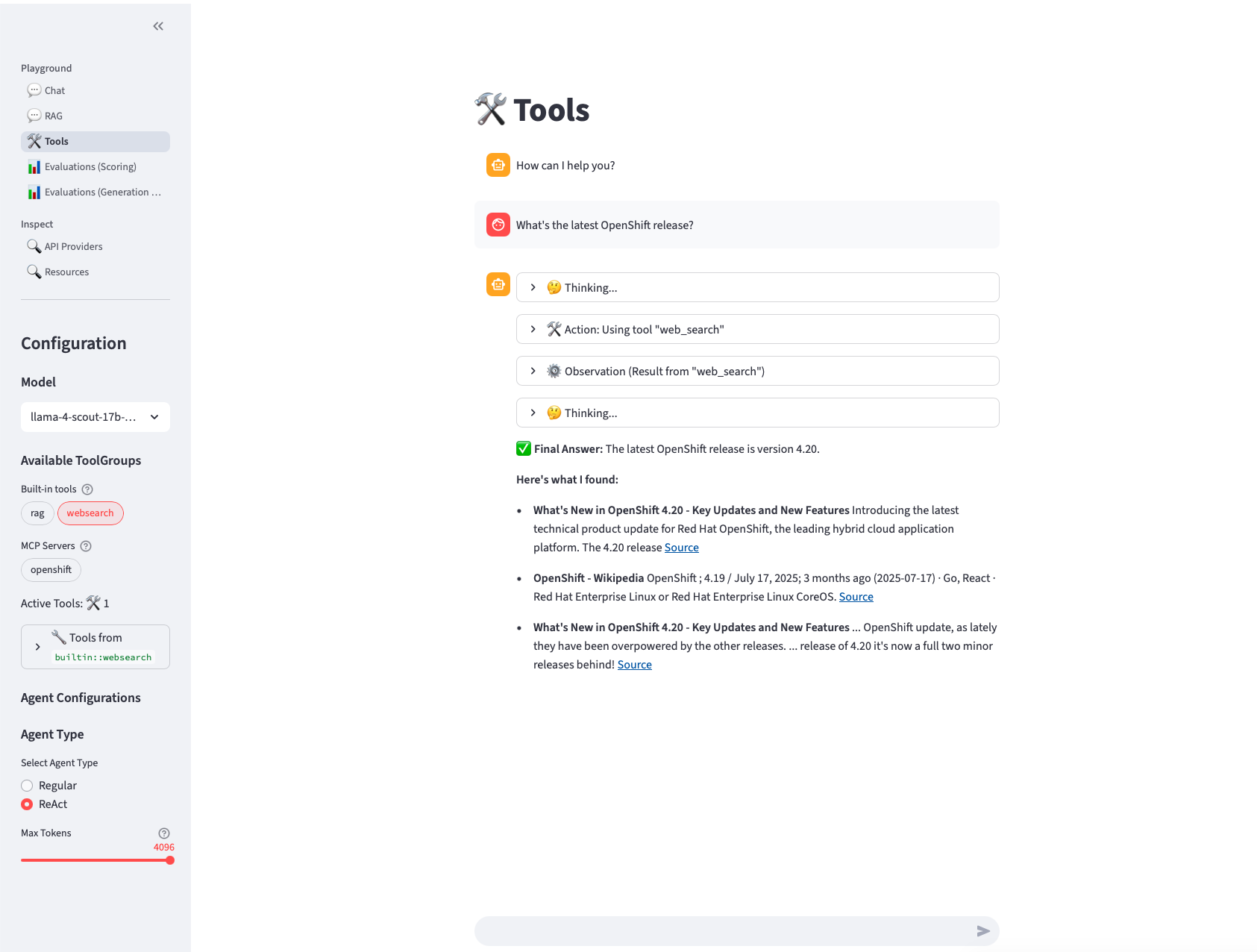
The ReAct agent can be used within the Llama Stack playground. Select the ReAct option within the Tool section to utilize it.
|
Use the |
You can see that the model follows the system instructions and plans the solving of the user prompt: