RHOAI Dashboard Configuration
RHOAI Dashboard Resources
Many of the objects in Red Hat OpenShift AI (RHOAI) are tied to an underlying Kubernetes resource. Because of this connection, many RHOAI objects can be created, updated, or deleted by performing the respective action on the underlying resource. Although some of these resources use a custom resource definition (CRD), many do not. For example, Data Science Projects are Red Hat OpenShift projects that include specific labels.
Idle Notebook Culling:
Notebooks and workbenches can consume many compute resources. Additionally, users might forget to shut them down when they are finished, which consumes cluster resources unnecessarily.
The Idle Notebook Culler helps reduce the number of inactive notebooks running on the cluster. It tracks the last time an action was taken in a notebook and shuts down the pods if the notebook has been inactive for a period of time. A notebook is considered inactive when no user has taken an action inside of the notebook. Actions include executing a cell, creating files, or interacting with the user interface.
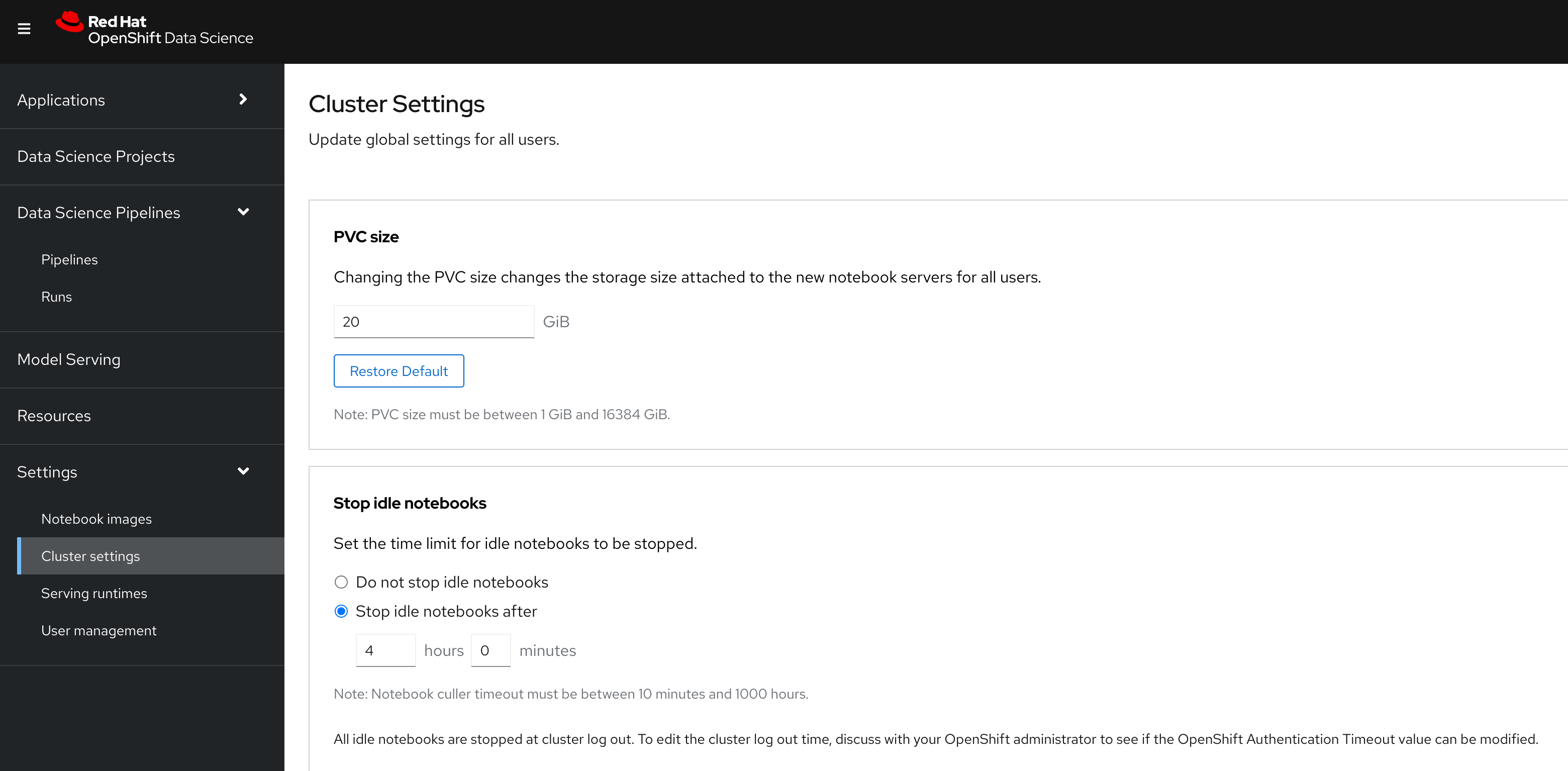
In RHOAI Dashboard>Settings>Cluster Settings>Stop idle notebooks:
When enabled is selected and saved, the ConfigMap below will be created. You can enable culling outside of RHOAI Dashboard by applying this ConfigMap to redhat-ods-applications namespace.
Apply ConfigMap in redhat-ods-applications.
CULL_IDLE_TIME and IDLENESS_CHECK_PERIOD is in minutes. ENABLE_CULLING is false by default.
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: notebook-controller-culler-config
namespace: redhat-ods-applications
labels:
opendatahub.io/dashboard: 'true'
data:
CULL_IDLE_TIME: '60'
ENABLE_CULLING: 'true'
IDLENESS_CHECK_PERIOD: '1'
In RHOAI Dashboard>Settings>Cluster Settings>Stop idle notebooks
If culling is enabled by ConfigMap, but then disabled in RHOAI Dashboard settings. The ConfigMap notebook-controller-culler-config will be deleted.
|
Workbench and Model Server Sizes
When launching workbenches or model servers from the RHOAI dashboard, users can select from several default sizes. These default options might not suit your organization’s needs. In such cases, you can use custom model server and notebook size configurations. To do this edit the odh-dashboard-config OdhDashboardConfig resource in namespace redhat-ods-applications. You can use the OpenShift Dashboard → Search or navigate to Home → API explorer and filter ford OdhDashboardConfig:
apiVersion: opendatahub.io/v1alpha
kind: OdhDashboardConfig
metadata:
annotations:
internal.config.kubernetes.io/previousKinds: OdhDashboardConfig
internal.config.kubernetes.io/previousNames: odh-dashboard-config
internal.config.kubernetes.io/previousNamespaces: default
name: odh-dashboard-config
namespace: redhat-ods-applications
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: rhods-dashboard
app.opendatahub.io/rhods-dashboard: 'true'
spec:
...output omitted...
modelServerSizes:
- name: Small
resources:
limits:
cpu: '2'
memory: 8Gi
requests:
cpu: '1'
memory: 4Gi
...output omitted...
notebookSizes:
- name: Small
resources:
limits:
cpu: '2'
memory: 8Gi
requests:
cpu: '1'
memory: 8Gi
...output omitted..After making changes and saving, give the RHOAI Dashboard a few minutes to update. The changes should now be available.