Connect to Workbench kernel from local VSCode
Some of the clients have expressed interest in connecting to remote workbench from their local environment (IDE’s) and execute the Jupyter Notebooks. The standard feature of most IDEs to connect to remote kernel uses token based authentication. Workbench pods running on RHOAI contain an authentication mechanism that sits in front of the workbench container and handles the authentication of the user connecting to the workbench. This container uses Openshift Authentication mechanism and is not compatible with the standard connection feature of most IDEs.
Steps to connect local VS Code to RHOAI Workbench kernel:
-
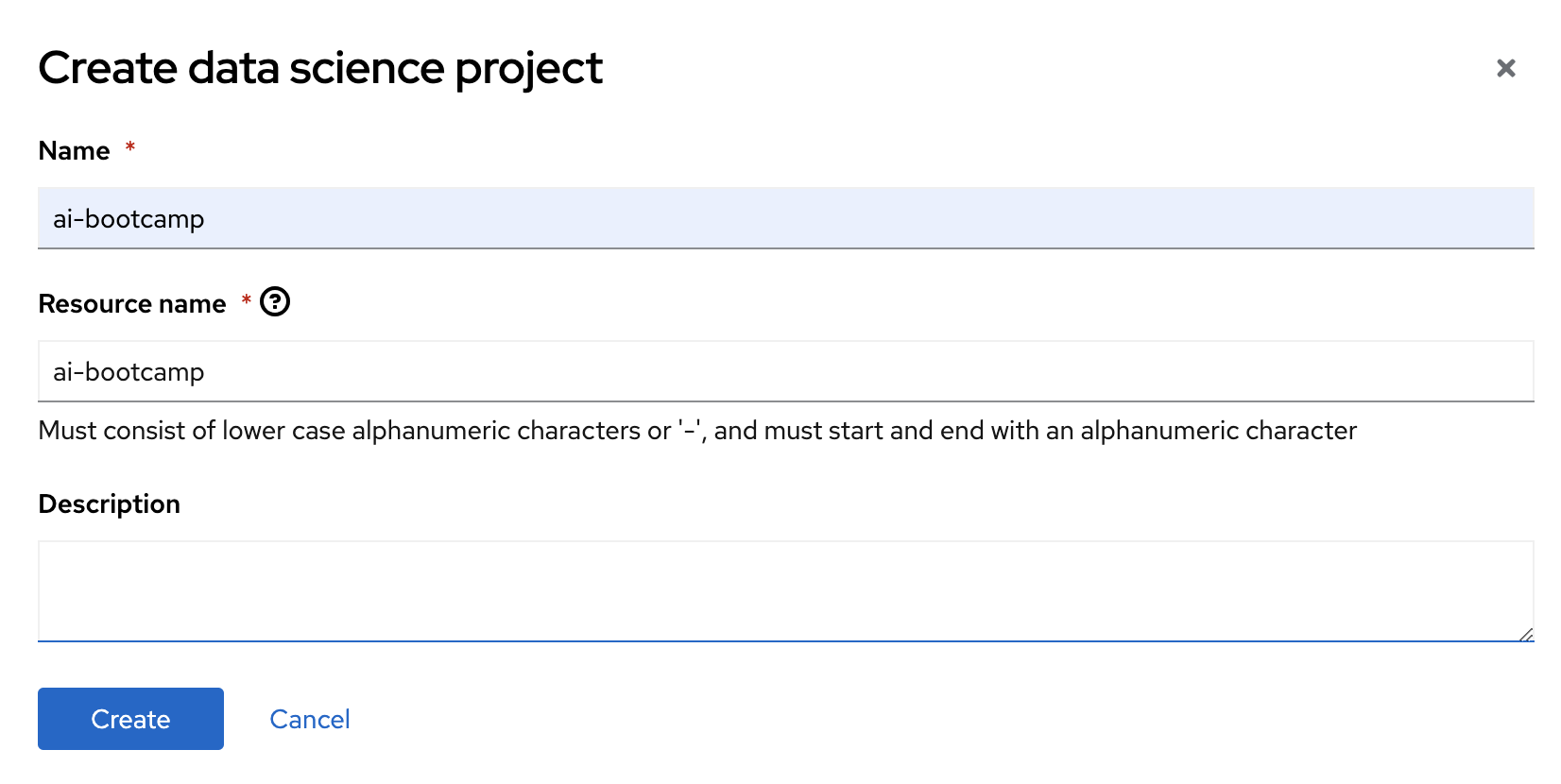
Create a Data Science Project ai-bootcamp
-
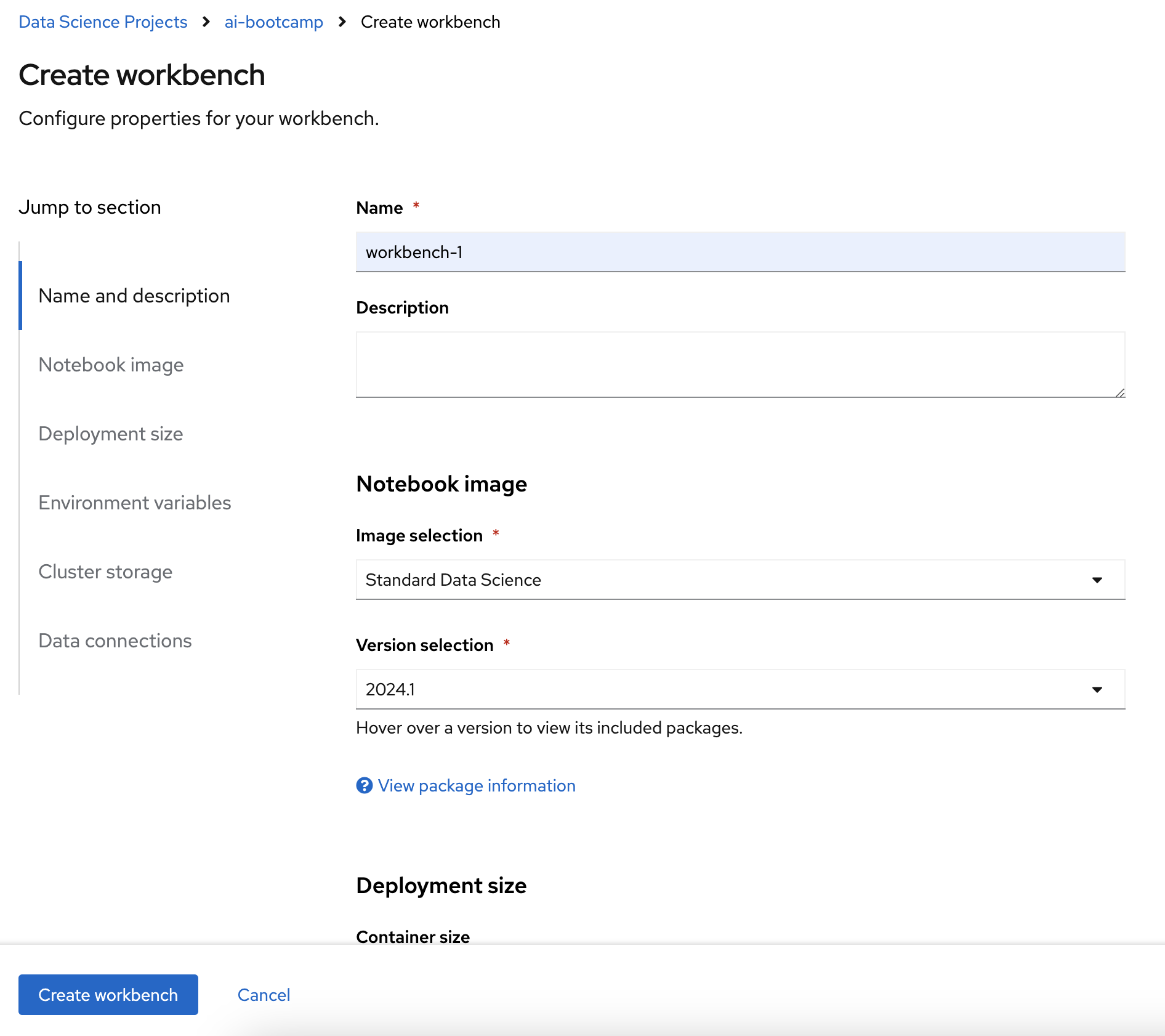
Create a workbench with following parameters: Name workbench-1 image Standard Data Science
-
Open VS Code in local. Create a new jupyter notebook.
-
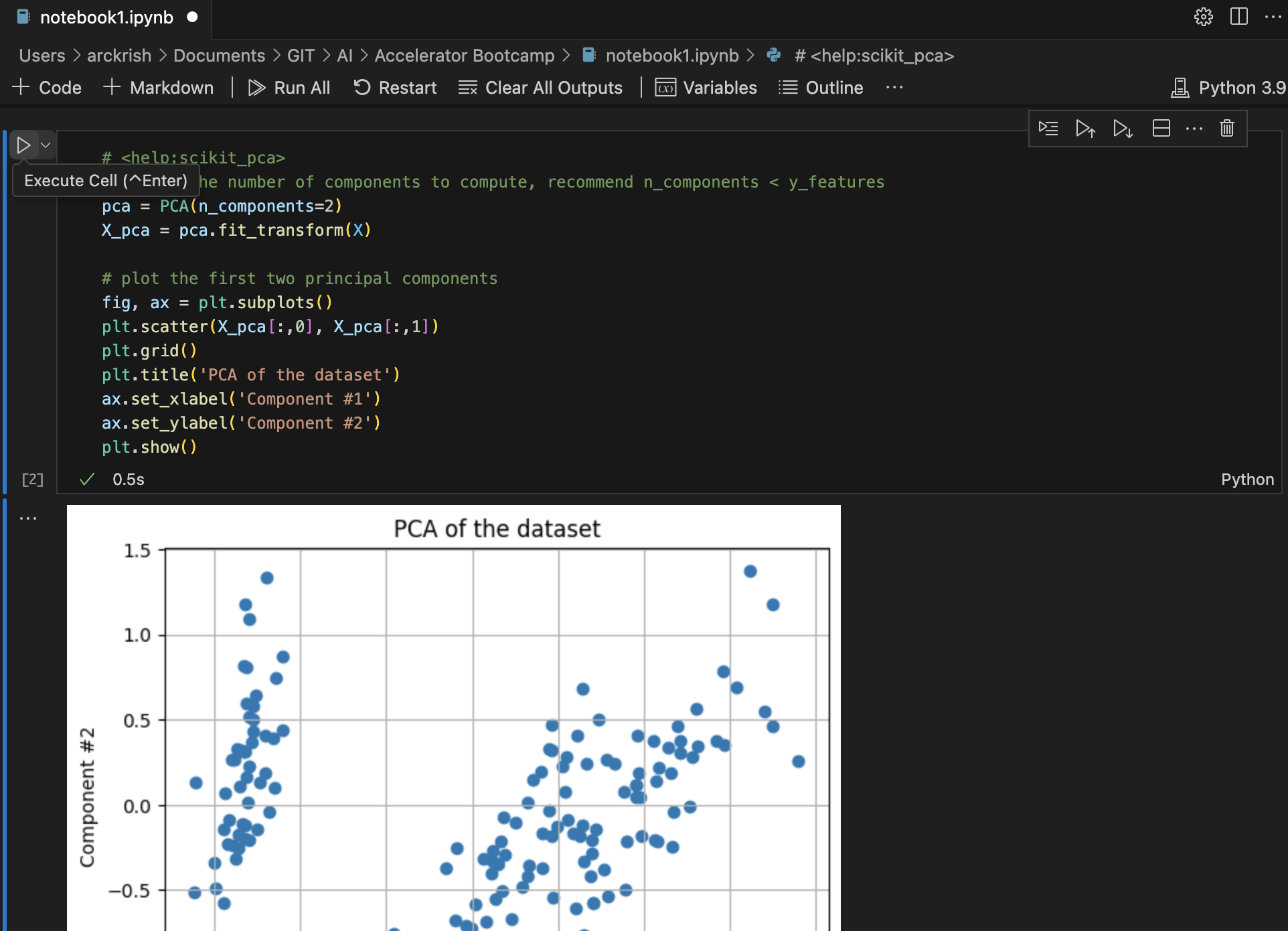
Principal Component Analysis Plots: This example uses Iris Data, performs a PCA and plots the data against the first two principal components in a scatter plot. It then prints the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the covariance matrix and finally prints the precentage of total variance explained by each component.
-
In a new cell, add the below contents.
from __future__ import division import math import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import sklearn.datasets import sklearn.metrics as metrics from sklearn.decomposition import PCA from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler # load the iris dataset dataset = sklearn.datasets.load_iris() # define feature vectors (X) and target (y) X = dataset.data y = dataset.target labels = dataset.target_names# <help:scikit_pca> # define the number of components to compute, recommend n_components < y_features pca = PCA(n_components=2) X_pca = pca.fit_transform(X) # plot the first two principal components fig, ax = plt.subplots() plt.scatter(X_pca[:,0], X_pca[:,1]) plt.grid() plt.title('PCA of the dataset') ax.set_xlabel('Component #1') ax.set_ylabel('Component #2') plt.show()# <help:scikit_pca> # eigendecomposition on the covariance matrix cov_mat = np.cov(X_pca.T) eig_vals, eig_vecs = np.linalg.eig(cov_mat) print('Eigenvectors \n%s' %eig_vecs) print('\nEigenvalues \n%s' %eig_vals)# <help:scikit_pca> # prints the percentage of overall variance explained by each component print(pca.explained_variance_ratio_) -
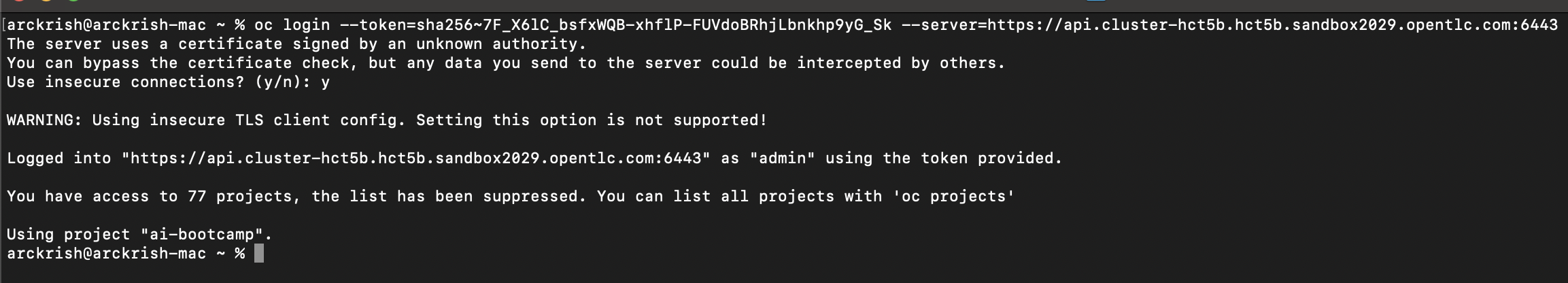
Login to OpenShift from terminal on your laptop.
-
Switch to project and view pods
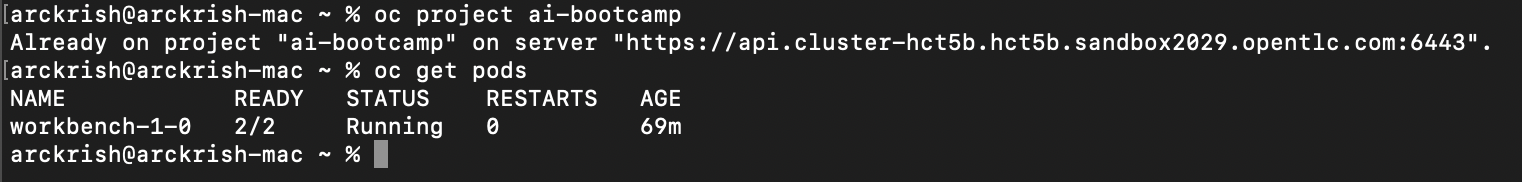
-
Start port-forwarding to the workbench pod You need to forward to the port the pod is listening on. It is usually 8888 for RHOAI workbench. You can find this port from the service in your project with name same as your workbench.
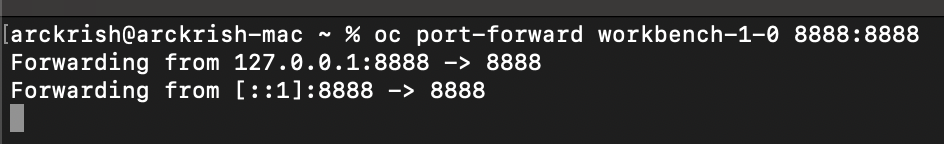
-
Open the Jupyter Notebook in your VSCode
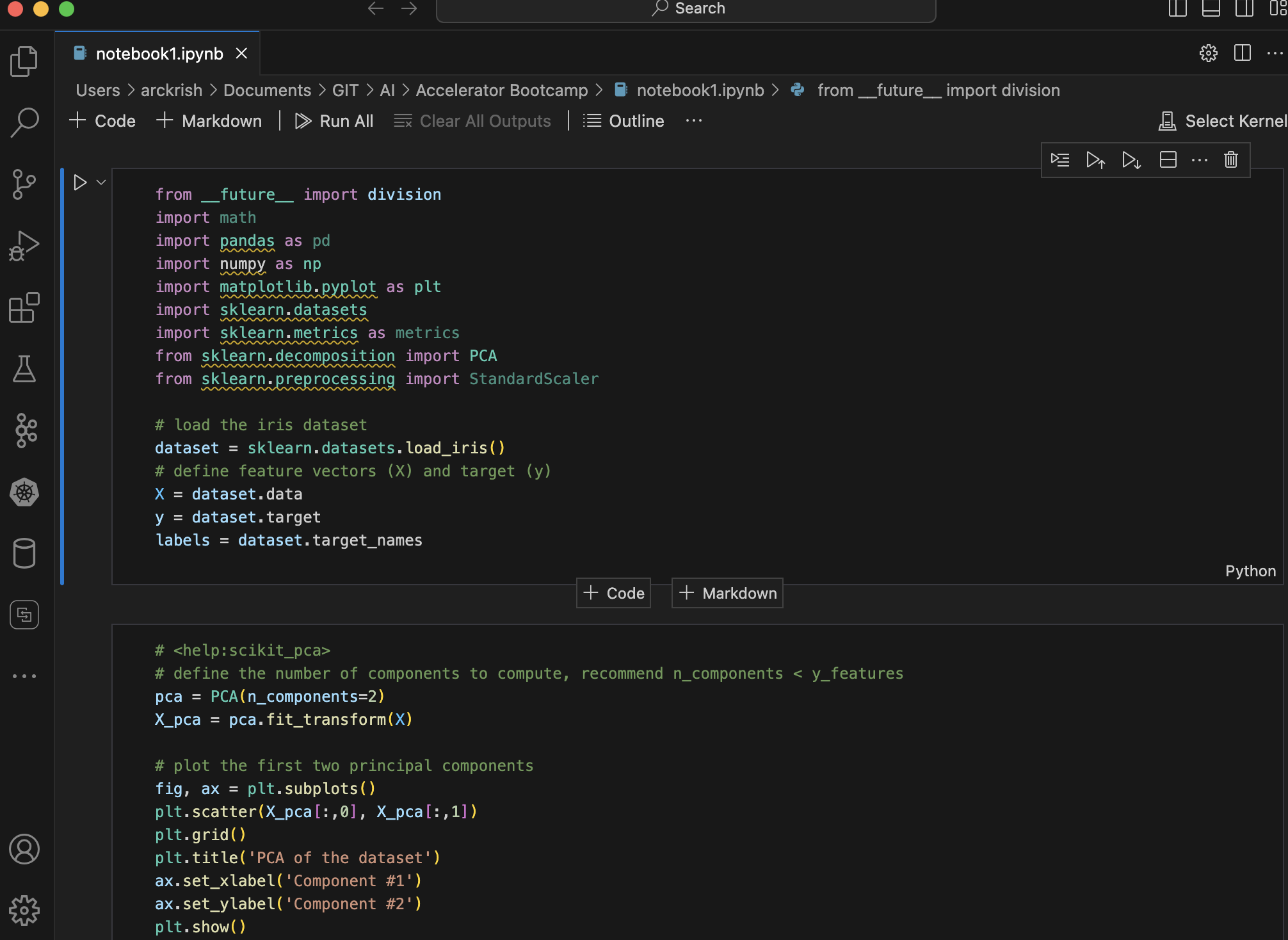
-
Click on Select Kernel in the top right corner of the notebook.
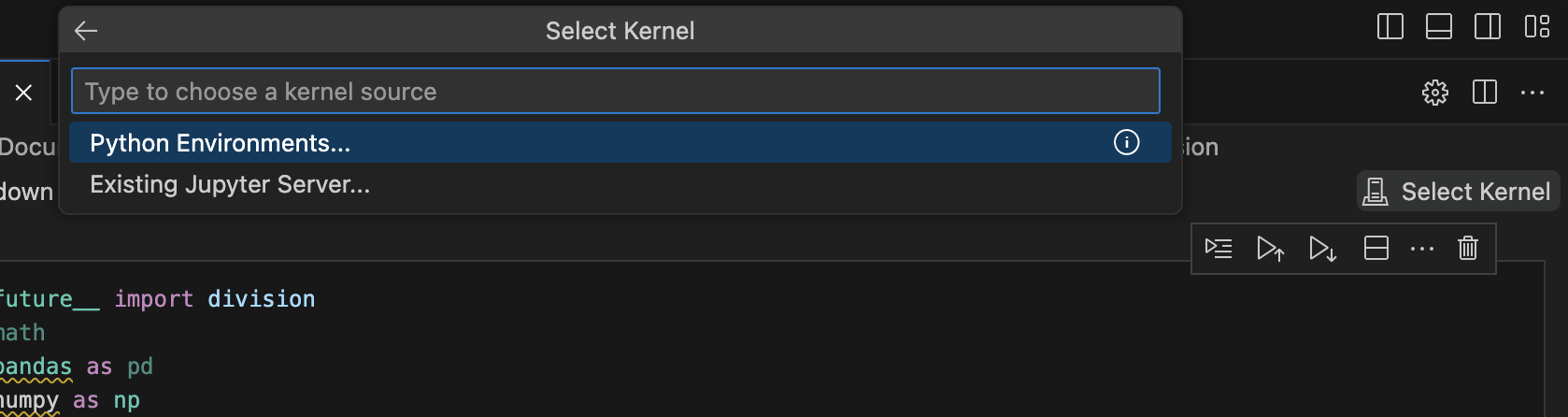
-
From the options, select Existing Jupyter Server and then enter the url as follows: localhost [:port] /context-path
In this case url is:
http://localhost:8888/notebook/ai-bootcamp/workbench-1/lab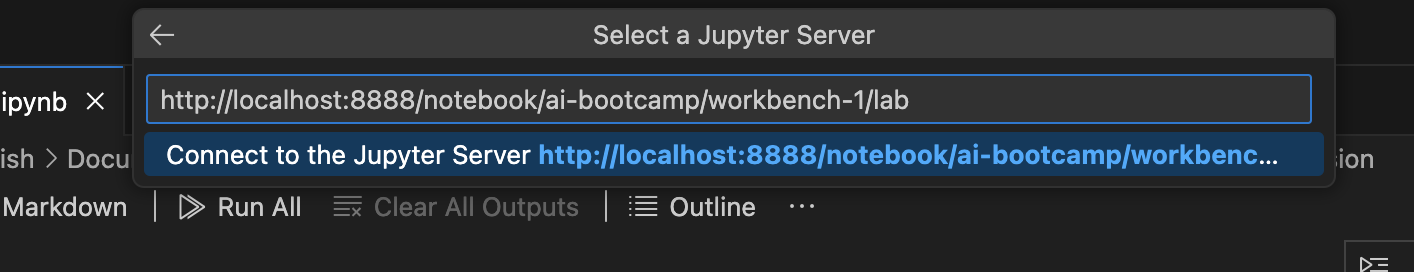
-
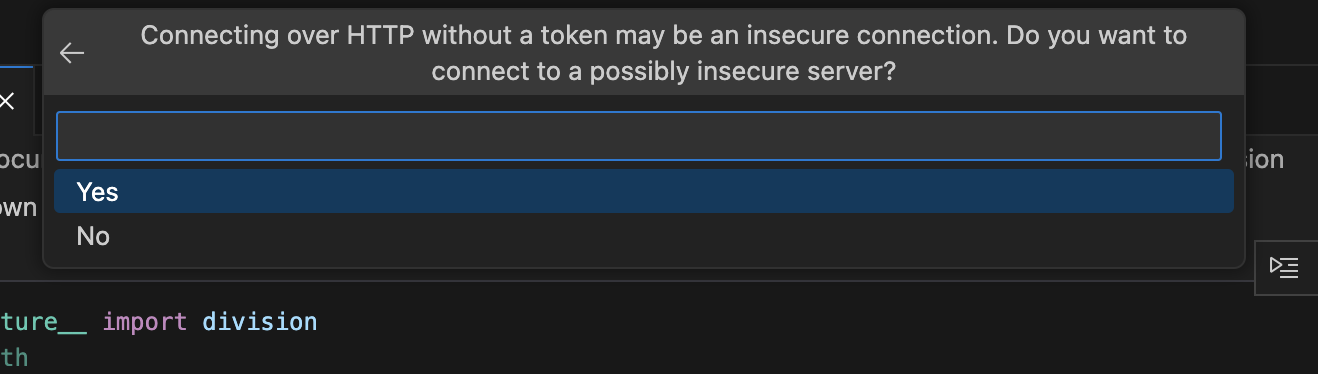
Select Yes for the prompt: Connecting over HTTP without a token may be an insecure connection. Do you want to connect to a possibly insecure server?
-
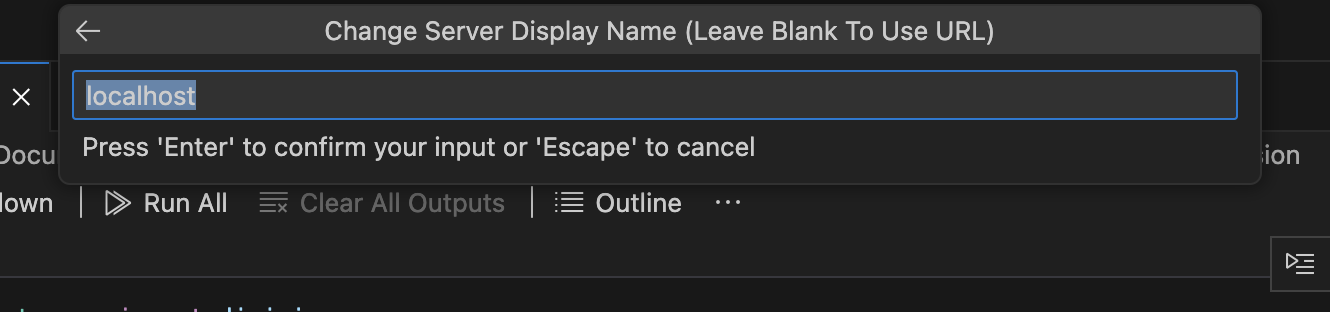
Choose a new name or click 'Enter' to accept the suggested server name.
-
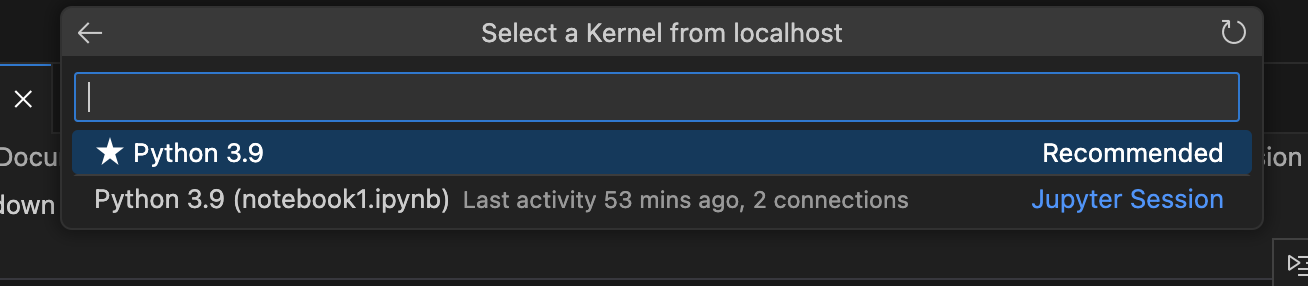
Choose Python 3.9 from the list of available kernels.
-
We should be able to see the selected kernel in top-right corner. Execute the cells in the notebook. This will execute using the remote kernel on the RHOAI workbench.