LLM GPU Requirements
When selecting hardware to run an LLM, several factors need to be considered including the model size, the KV Cache requirements for the use case, the use case concurrency requirements, the format of the model’s data types, and any performance requirements such as Time to First Token (TTFT) or throughput.
Estimating Model Size
One of the first calculations needed to help understand if a model will run on a particular GPU is creating an estimate of the model size.
The size of the model loaded into vRAM can be estimated using the following formula:
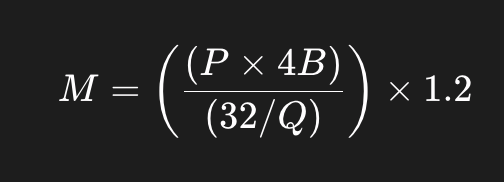
Symbol |
Description |
M |
GPU memory |
P |
The number of parameters in the model |
4b |
4 bytes, expressing the bytes used for each parameter |
32 |
There are 32 bits in 4 bytes |
Q |
The amount of bits that should be used for loading the model. - 16 bits, 8 bits or 4 bits. |
1.2 |
Represents a 20% overhead of loading additional things in GPU memory. |
For example, for Granite 3.3 8B Instruct is 8 billion parameters and is an fp16 model.
(((8*10^9*4)/(32/16))*1.2) / 1024^3 = 17.9 GbFor some additional details on this calculation, you can read more about it here.
Quantization
Some LLMs will use quantization to make them smaller and more performant. Most models will default to an fp16 data type which uses 16 bits, but fp8 is a common quantization option that use 8 bit data types. Int4 is another common data type that is gaining popularity which uses only 4 bits. Additionally, some advanced techniques can be uses such as the w4a16 which primarily use an int4 data type but also leverage some additional bits to increase the performance compared to traditional int4 models.
Estimating KV Cache
Beyond the model itself, vLLM also requires vRAM for the KV Cache. The KV Cache requires a specific amount of vRAM per token that can be different from model to model. An estimate for the vRAM per token can be calculated based on the architecture of the model with details from the config.json file on HuggingFace.
This class will not dig into details of calculating the vRAM per token, but you can read more here to better understand how to calculate that value.
In addition to the vRAM per token, you will need to understand the context length requirements for the use case. By default vLLM will use the max context length for the model, but if you are running the model on a smaller GPU, you may need to limit the KV Cache to a smaller context length.
Granite 3.3 8B Instruct requires 0.15625 Mb per token and the models max context length is 131,072, giving us a requirement of 20 Gb of vRAM for the KV Cache.
Along side our model requirements of about 17.9 Gb, that means we need about 38 Gb to run the model and support the max context length.
Sizing Spreadsheet
Red Hat Services has created a spreadsheet to help do sizing estimates for LLMs that you can find here:
Using the "Model Sizing" tab, you can select several different models to perform a sizing calculation. The spreadsheet will provide recommendations based on the model you have selected and the models max context length.
You can update the context length requirements to override the default.
Additionally, vLLM allows users to use a quantized KV Cache to increase the total number of tokens supported with the same vRAM.
In addition to the model sizing, the "Subs & Cost Modeling" tab will help to recommend instance types needed to run your selected model in different environments. The "Subs & Cost Modeling" tab can help to provide a Total Cost of Ownership of running the models on OpenShift including both cloud computing costs, OpenShift subs, and OpenShift AI subs.
Please keep in mind that all costs are subject to change and the cost is simply an estimate and should not be used in a quote to a customer.