GPU Sharing
GPU Sharing Overview
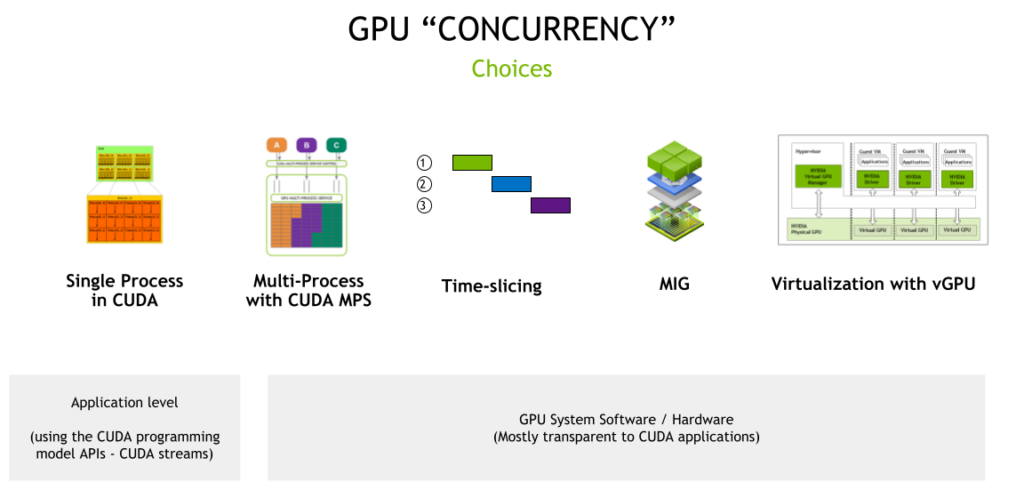
GPU sharing is a technique that allows multiple workloads to share a GPU. This is useful for small workloads that don’t require full GPU power simultaneously. This can be broken down into three maing components:
-
Time-slicing
-
Multi-Instance GPUs (MIG)
-
CUDA Multi-Process Service (MPS)
Pros and Cons of GPU Sharing Methods
| Strategy | Benefits | Cons |
|---|---|---|
Time-slicing |
Allows multiple workloads to share a GPU by interleaving execution. |
No isolation between workloads sharing the same GPU, leading to potential crashes affecting all workloads. |
Useful for small workloads that don’t require full GPU power simultaneously. |
Less control over resource allocation, making it less suitable for production environments. |
|
Can lead to contention and suboptimal performance if workloads compete for GPU resources. |
||
Not recommended for most GPU sharing scenarios. |
||
Multi-Instance GPUs (MIG) |
Provides strict isolation between workloads by partitioning the GPU into smaller instances. |
Only supported on NVIDIA Ampere GPUs. |
Each instance behaves like a separate GPU with its own memory and compute resources. |
Less flexible than CUDA Multi-Process Service (MPS). |
|
Ensures memory protection and error isolation. |
Requires proper configuration and understanding of the underlying GPU architecture. |
|
Suitable for workloads with varying resource requirements and need for isolation. |
Limited to specific GPU models (e.g., A100). |
|
CUDA Multi-Process Service (MPS) |
Enables fine-grained sharing of GPU resources among multiple pods by running CUDA kernels concurrently. |
Does not provide full memory protection and error isolation between processes. |
Feels similar to CPU and memory resource allocation in Kubernetes. |
Sharing with MPS is not supported on devices with MIG enabled. |
|
Supported on almost every CUDA-compatible GPU. |
May not be suitable for workloads requiring strict isolation. |
|
Suitable for efficiently sharing GPU resources without strict isolation requirements. |
Requires careful management to avoid resource contention and ensure optimal performance. |