3Scale API Gateway
In this module, you will learn how to configure 3Scale API Gateway to give access to the models previously deployed in the first lab.
3Scale Overview
Connection to 3Scale Admin Portal
3Scale is an API management platform that provides a way to manage, secure, and analyze APIs. It allows you to create and manage API keys, set up rate limits, and monitor API usage.
To connect to the 3Scale admin portal, you will need the admin_user and admin_password values. They can be found in the system-seed secret in the 3scale namespace.
-
From a Terminal (in your VSCode workbench) log into OpenShift.
oc login -u {user} -p {password} --server={openshift_api_url}(approve the certificate when prompted to allow insecure connections)
-
Now that you are logged in, you can get the secret values with the following commands:
oc get secret system-seed -n 3scale -o template='{{range $key, $value := .data}}{{if or (eq $key "ADMIN_USER") (eq $key "ADMIN_PASSWORD")}}{{printf "%s: " $key}}{{ $value | base64decode }}{{"\n"}}{{end}}{{end}}'
Now you can log into the 3Scale admin portal at https://maas-admin.{openshift_cluster_ingress_domain}/ using the credentials you just retrieved.
You will be prompted by a wizard window. Close it by clicking on the top right corner of the screen.
Enabling access to the Developer Portal
Developer Portal allows API providers to create a customizable, branded interface for onboarding developers, sharing API documentation, and managing access credentials. It supports content management, theming, and integration with backend services to streamline API consumption.
A user was already created for you in 3Scale in (Audience→Accounts→Listing), but you still need to configure the developer portal to allow users to access it.
-
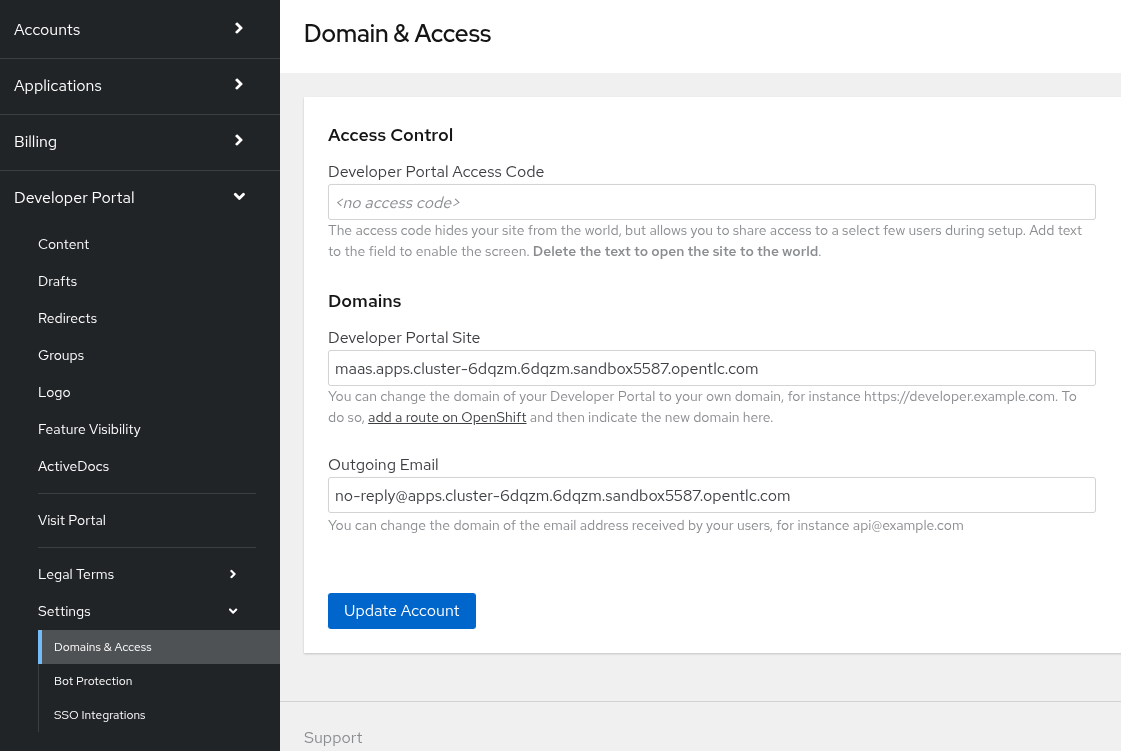
On the Audience section, got to Developer Portal→Settings→Domains & Access.
-
The Developer Portal Access Code is used to control the access the developer portal. Simply delete it and click on
Update Account. to remove the access code and allow anyone to access the developer portal, although they will still need to authenticate.
Configuring 3Scale
You are ready to create a new Product based on the model you deployed in the previous module. To do that we are going to use the 3Scale operator. This will show you how you can fully automate the deployment of new models in your service.
The order of deployment is
-
Create Backend → Address of the hosted model
-
Create Product → Defines the mapping rules, security, metrics and policies for the model endpoint
-
Create API document → OpenAPI definition of the service
-
Create API ProxyConfigPromote → Promotes the product into production
Creating the backend for the product
-
Edit the following yaml to add the address of your hosted model and then paste the yaml into the UI.
kind: Backend
apiVersion: capabilities.3scale.net/v1beta1
metadata:
name: llama70b
namespace: 3scale
spec:
name: LLama70B
privateBaseURL: 'your url goes here'
systemName: llama70bCreating a new Product in 3Scale
Copy and paste the following yaml into the UI
apiVersion: capabilities.3scale.net/v1beta1
kind: Product
metadata:
name: llama70b
namespace: 3scale
spec:
name: LLama70B
systemName: llama70b
metrics:
hits:
description: Number of API hits
friendlyName: Hits
unit: hit
deployment:
apicastHosted:
authentication:
userkey:
authUserKey: Authorization
credentials: headers
backendUsages:
llama70b:
path: /
mappingRules:
- httpMethod: GET
increment: 1
metricMethodRef: health
pattern: /health
- httpMethod: POST
increment: 1
metricMethodRef: tokenize
pattern: /tokenize
- httpMethod: POST
increment: 1
metricMethodRef: detokenize
pattern: /detokenize
- httpMethod: GET
increment: 1
metricMethodRef: models
pattern: /v1/models
- httpMethod: GET
increment: 1
metricMethodRef: version
pattern: /version
- httpMethod: POST
increment: 1
metricMethodRef: chat/completions
pattern: /v1/chat/completions
- httpMethod: POST
increment: 1
metricMethodRef: completions
pattern: /v1/completions
- httpMethod: POST
increment: 1
metricMethodRef: embeddings
pattern: /v1/embeddings
policies:
- configuration:
allow_credentials: true
allow_headers:
- Authorization
- Content-type
- Accept
allow_methods: []
allow_origin: '*'
enabled: true
name: cors
version: builtin
- configuration: {}
enabled: true
name: remove-bearer
version: '0.1'
- configuration: {}
enabled: true
name: apicast
version: builtin
- configuration:
connect_timeout: 180
read_timeout: 180
send_timeout: 180
enabled: true
name: upstream_connection
version: builtin
methods:
chat/completions:
friendlyName: Chat Completions
completions:
friendlyName: Completions
detokenize:
friendlyName: Detokenize
embeddings:
friendlyName: Embeddings
health:
friendlyName: Health
models:
friendlyName: Models
tokenize:
friendlyName: Tokenize
version:
friendlyName: Version
applicationPlans:
standard:
appsRequireApproval: false
name: Standard Plan
published: trueCreating the API document for the product
-
Copy and paste the yaml into the UI.
apiVersion: capabilities.3scale.net/v1beta1
kind: ActiveDoc
metadata:
name: llama70b
namespace: 3scale
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: 3scale
spec:
activeDocOpenAPIRef:
url: 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/redhat-ai-services/etx-serving-at-scale/refs/heads/main/manifests/llama70b-chat.json'
name: llama70b
productSystemName: llama70b
published: true
skipSwaggerValidations: true
systemName: llama70bFinally create the ProxyConfigPromote
When a new Product is created, it is only available in a "staging" environment. This means that it is not yet available to the users. You need to publish it to make it available. This is done via a ProxyConfigPromote resource
-
Copy and paste the yaml into the UI.
kind: ProxyConfigPromote
apiVersion: capabilities.3scale.net/v1beta1
metadata:
name: llama70b
namespace: 3scale
spec:
productCRName: llama70b
production: trueuut* Finally, we must subscribe our user to this new product, as we did previously for Granite. Again, this is normally something you would automate as part of a deployment of a new product, but here we are going to do it in the 3Scale Admin Portal. Go to Audience→Listing, select user1 account.
+
-
In the account section, select the
Service Subscriptionstab at the right.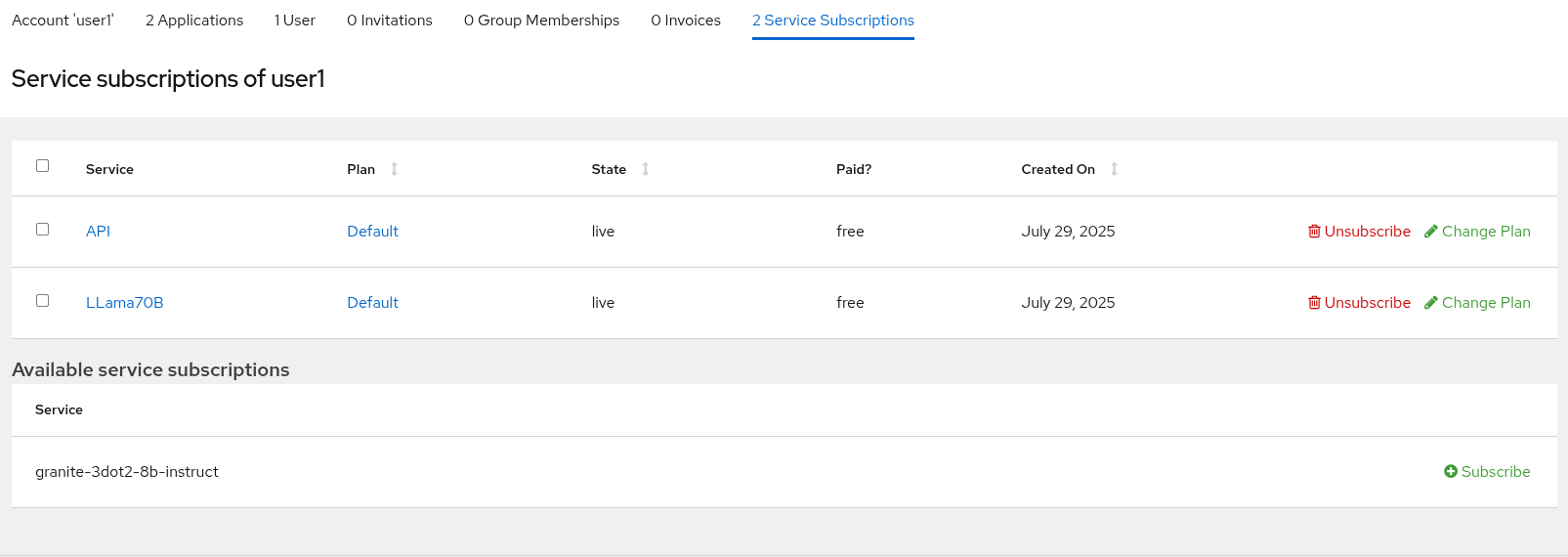
-
At the bottom right of the page, click on the
Subscribebutton on theLLama70Bitem. -
Finally select the
DefaultPlan and click onCreate subscription.
Testing the Product
You can now test this new Product in the same way you did for Granite in the previous module.
-
Connect to the Developer Portal at
https://maas.{openshift_cluster_ingress_domain}and log in using your credentials. -
Click on the
See your Applications and their credentialslink on the front page. -
Click on the
Create new applicationbutton. -
Select the
LLama70Bservice.
-
Enter a name for your application, for example
LLama70B application. Click onCreate Application. -
Your application has been created. You can see the Endpoint URL you can use to connect to the API, the name of the model you must use in your requests, and the API key that has been generated for you. You can now use this key to access the API.

-
You can now test the API using the
curlcommand in your terminal. Open a terminal in your VSCode environment (or on your laptop) and run the following command, replacing the placeholder values with the ones you got from the previous step:curl -X 'POST' \ '___ENDPOINT_URL___/v1/completions' \ -H 'accept: application/json' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -H 'Authorization: Bearer ___API_KEY___' \ -d '{ "model": "___MODEL_NAME___", "prompt": "San Francisco is a", "max_tokens": 15, "temperature": 0 }'
Example:
curl -X 'POST' \
'https://tinyllama-maas-apicast-production.apps.cluster-br294.br294.sandbox5291.opentlc.com:443/v1/completions' \
-H 'accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer 5924457cf136e9906c5c98cc5924ab7a' \
-d '{
"model": "tinyllama/tinyllama-1.1b-chat-v1.0",
"prompt": "San Francisco is a",
"max_tokens": 15,
"temperature": 0
}'Congratulations! You have successfully created a new Product in 3Scale and connected it to the Llama70B model.