Inference Server on Multiple Platforms
Existing lab resources
-
RH Inference server on multiple platforms
https://github.com/redhat-ai-services/inference-service-on-multiple-platforms -
RH Inference server tutorial
https://docs.google.com/document/d/11-Oiomiih78dBjIfClISSQBKqb0Ij4UJg31g0dO5XIc/edit?usp=sharing
Host Verification
Before proceeding, it is critical to verify that the host environment is correctly configured. Check Driver Status: After the system reboots, run the nvidia-smi (NVIDIA System Management Interface) command. A successful configuration will display a table listing all detected NVIDIA GPUs, their driver versions, and CUDA versions.14
nvidia-smi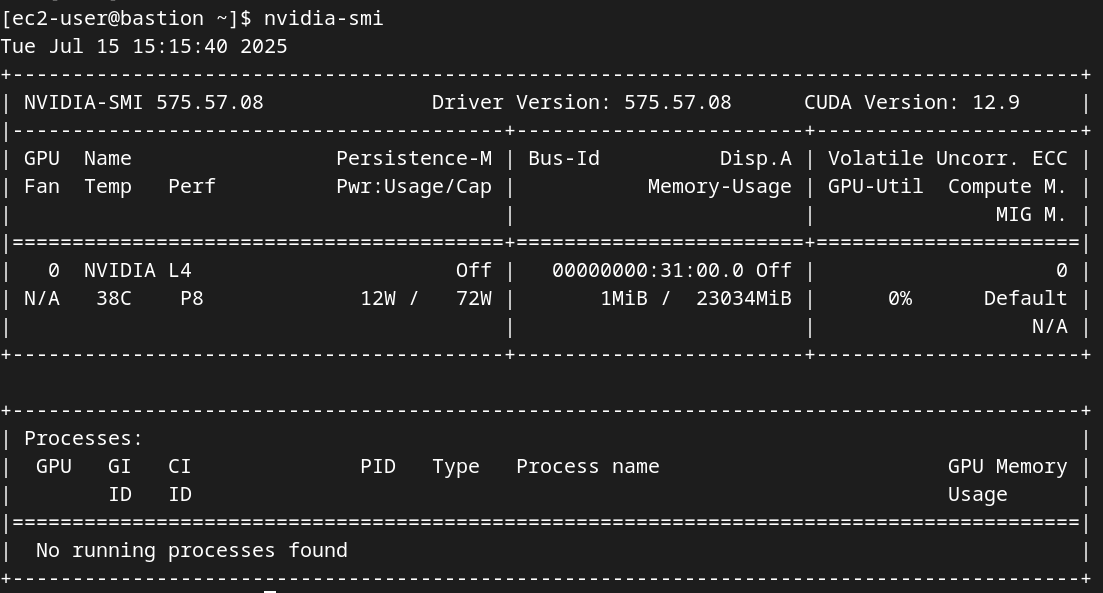
Install nvidia-container-toolkit
The NVIDIA Container Toolkit is the crucial bridge that allows container runtimes like Podman or Docker to securely access the host’s GPUs.
curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/libnvidia-container/stable/rpm/nvidia-container-toolkit.repo | \
sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/nvidia-container-toolkit.repo
sudo dnf-config-manager --enable nvidia-container-toolkit-experimental
sudo dnf install -y nvidia-container-toolkitConfigure CDI
sudo nvidia-ctk cdi generate --output=/etc/cdi/nvidia.yaml
# check the config
nvidia-ctk cdi list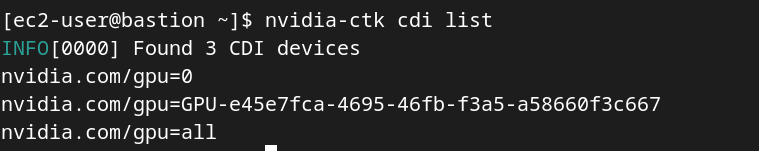
Test Container-GPU Access: To confirm that Podman can access the GPUs, run a simple test workload using a standard NVIDIA CUDA sample image. This step definitively validates the entire stack, from the driver to the container runtime.
sudo podman run --rm --device nvidia.com/gpu=all nvcr.io/nvidia/k8s/cuda-sample:vectoradd-cuda11.7.1-ubi8
podman run --rm -it \
--security-opt=label=disable \
--device nvidia.com/gpu=all \
nvcr.io/nvidia/cuda:12.4.1-base-ubi9 \
nvidia-smi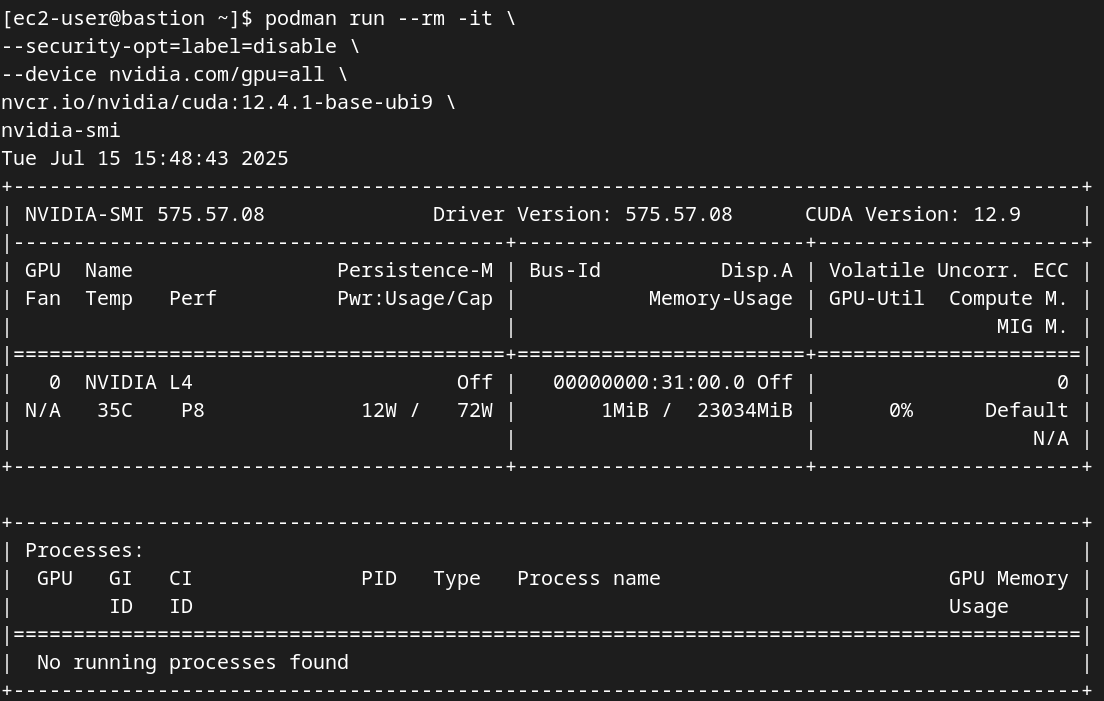
Logging Into Red Hat Container Registry
Login to registry.redhat.io
sudo podman login registry.redhat.ioRunning vLLM on RHEL
Clone the repository with RH Inference server for RHEL
git clone https://github.com/redhat-ai-services/etx-llm-optimization-and-inference-leveraging.gitRun the vllm pod
sudo podman kube play etx-llm-optimization-and-inference-leveraging/optimization_lab/rhel/vllm-pod.yamlOpen a new terminal to follow the logs.
sudo podman logs --follow vllm-vllmcurl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{
"prompt": "What is the capital of France?",
"max_tokens": 100
}' http://127.0.0.1:80/v1/completions | jqGo to your other terminal and view the logs. You should see a successful log entry.
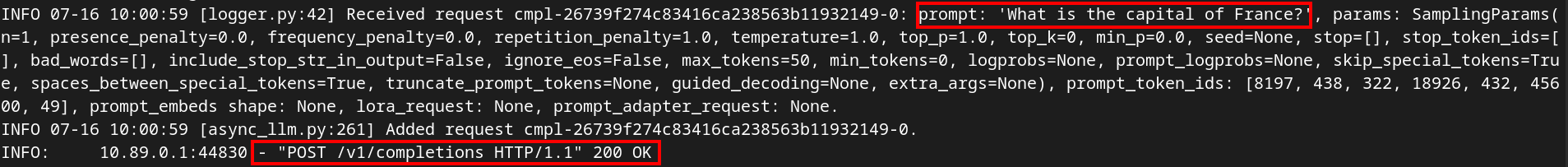
Run a quick benchmark test
We’ll run a quick benchmark test to show how the RH Inference server performs.
pip install guidellmRun a default benchmark
guidellm benchmark \
--target "http://127.0.0.1:80/v1" \
--model "granite-3.0-2b-instruct" \
--rate-type sweep \
--max-seconds 30 \
--data "prompt_tokens=256,output_tokens=128"Remove and cleanup vllm pod
sudo podman pod stop vllm && sudo podman pod rm vllm Follow logs
sudo podman logs --follow vllm-vllm curl http://localhost/version # this is accessible from the internet curl http://<public-ip-address>/version